Encryption
Introduction
The Encryption service is responsible to encrypt the data in order to make them unreadable to an unauthorized person or entity. It converts the original data, known as plaintext to encoded text called ciphertext by using encryption techniques and algorithms. In order to get back the original data, the ciphertext must be decrypted.
Our Encryption service runs only on-premise through a registered runner, instead of as standalone docker container. In order to run, it needs a JSON configuration file as input. As an output, it produces and stores the encrypted file in MinIO and communicates the execution state as feedback to the Backend service, through RabbitMQ. The Encryption service is implemented in python.
Background
There are two types of data encryption, the symmetric and asymmetric encryption. The main difference between the two methods is whether or not the same key is used for encryption and decryption. In symmetric encryption the same key, called symmetric key, is used for encryption and decryption. On the other hand, the asymmetric encryption uses a private-public key pair to encrypt/decrypt the data. The private key is kept secret by the owner, as it is responsible for decrypting the data and the public key is shared to other people in order to encrypt the data that they want to send to the owner of the private key.
Requirements
A list of services that need to be deployed (running), in order for the Encryptor to be fully functional:
Functionality
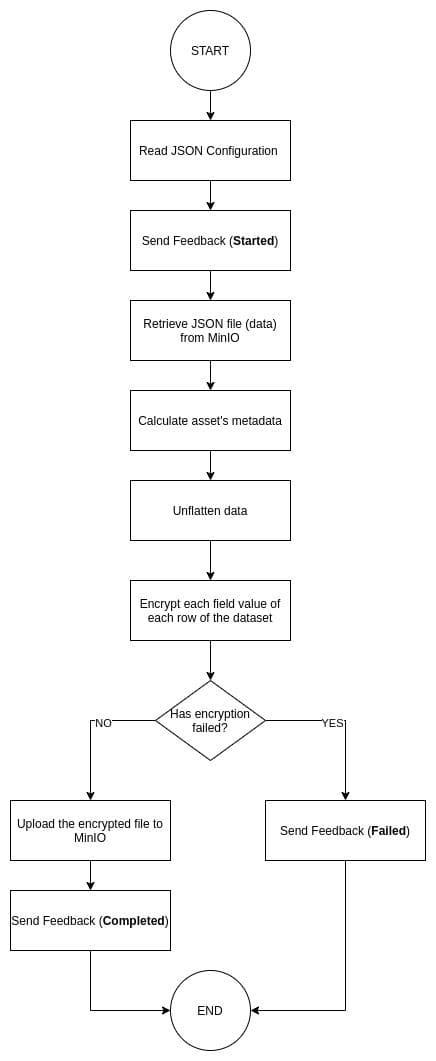
First, at the runner registration, a private-public key pair is created on the runner's side. The private key is stored in the runner's machine keychain and the public key is sent to the platform. The platform saves the public key in the postgres database. Each time a data check-in job (with the Encryption step selected) is created, a new symmetric key is generated. The platform stores the symmetric key in the Vault (unencrypted), encrypts the symmetric key using the public key of the runner and appends it to the JSON configuration of the job. Then, the encryption service receives the JSON configuration and the data as a single file that the previous step has stored in MinIO. It calculates the asset's metadata before starting the encryption process. Then, it unflattens the data and encrypts each field value of each row of the data individually. Finally, the encrypted data (file) is uploaded to the MinIO (/loader path). If the encryption process fails for any reason, the step fails and the failure details are sent instread.
Configuration File
A JSON configuration file is required from the Encryption service. The requirements of the configuration file are described in the schema.py file that exists in the Encryption Project.